The Indian Railways has launched a cutting-edge AI-driven predictive maintenance system across major train routes and workshops. The system, designed to anticipate equipment failure before it occurs, is part of the Railways’ broader initiative to bring “zero-accident” operations through intelligent automation, sensors, and data analytics.
Officials describe the move as a “revolutionary leap from repair to prediction,” marking the largest-scale AI deployment in India’s public transport sector.
New Delhi, October 23 —
In a decisive move toward modernising one of the world’s largest railway networks, the Indian Railways has rolled out an AI-powered predictive maintenance system aimed at eliminating derailments, reducing downtime, and saving crores in maintenance costs.
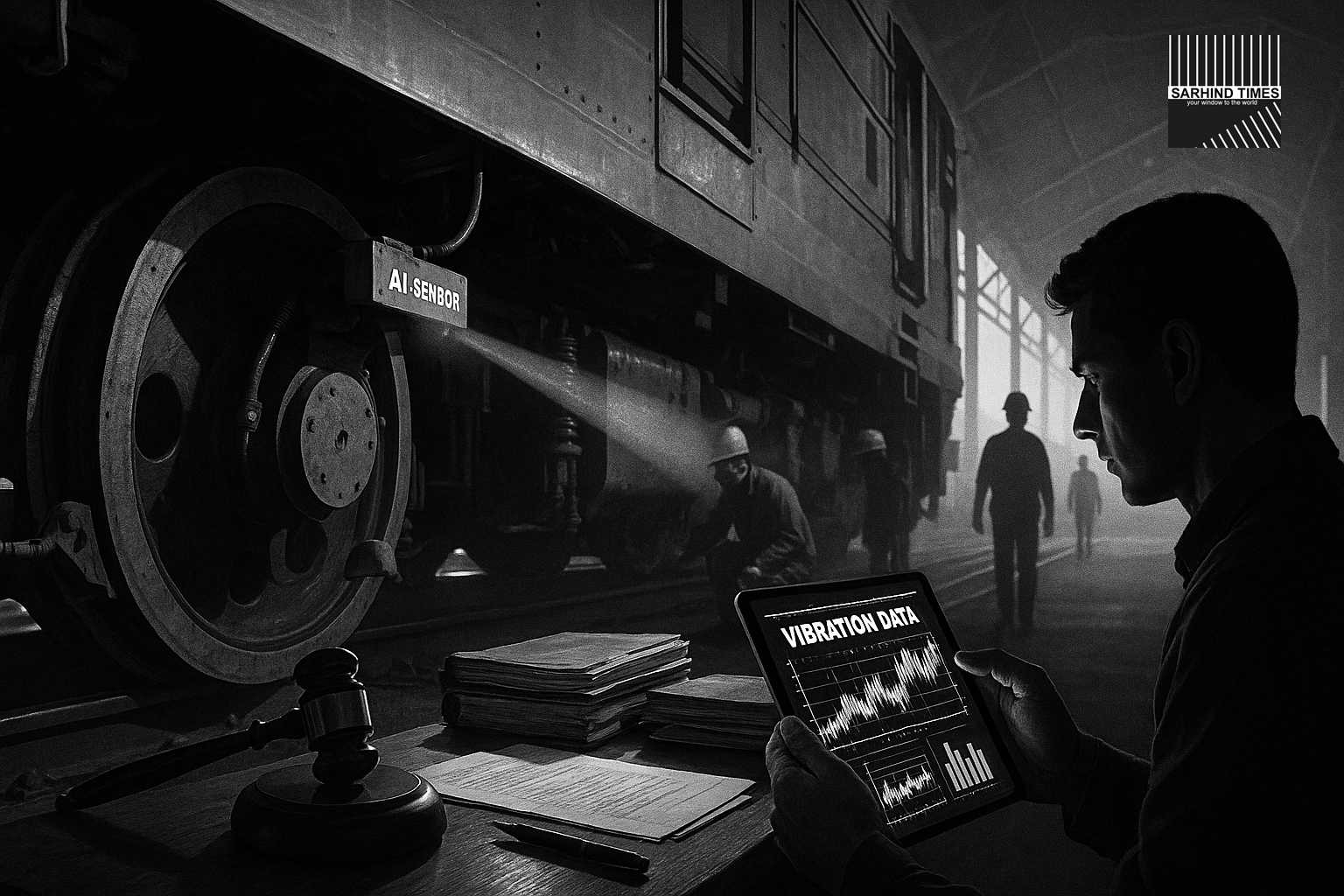
The system, developed in partnership with IIT Madras, RailTel, and Tata Elxsi, analyses data from thousands of sensors embedded in locomotives, wagons, and tracks to predict mechanical failures before they happen.
“We are replacing reactive maintenance with intelligent prevention,” said Railway Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw at the launch event.
“This is not just technology — it’s transformation.”
1. Why Predictive Maintenance Matters
India’s railway network carries over 23 million passengers daily and 1.2 billion tonnes of freight annually.
Mechanical failures, track fatigue, and signal malfunctions have historically been major contributors to accidents and delays.
The new system uses machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies such as:
- Bearing vibrations,
- Temperature fluctuations,
- Axle pressure deviations, and
- Wheel wear patterns.
Once a fault trend is identified, the AI system automatically flags it to the nearest depot for preventive action.
“AI is the new wrench in the engineer’s hand,” said Vinay Kumar, Chief Mechanical Engineer, Northern Railways.
“We no longer wait for a sound or smoke to signal trouble.”
2. How It Works
The predictive maintenance platform integrates data from:
- IoT sensors installed on rolling stock,
- Trackside acoustic monitors,
- Thermal imaging cameras, and
- Vibration detectors on bridges and turnouts.
The AI continuously analyses data in real time to calculate “health scores” for every critical asset — from engines to couplings.
If a threshold is breached, alerts are sent to control centres and maintenance teams via the Railway Data Command Hub (RDCH).
The system runs on AWS GovCloud architecture, ensuring high data reliability and compliance with government security protocols.
3. The First Pilot: South Central Zone
The program was first tested in the South Central Railway Zone last year across Visakhapatnam, Vijayawada, and Secunderabad divisions.
Within six months, officials reported:
- 38% reduction in unscheduled maintenance,
- 27% decline in track-related failures, and
- 25% increase in locomotive uptime.
“What used to take days of manual inspection now takes seconds,” said General Manager Arun Kumar Jain.
“The AI doesn’t blink — it sees everything, all the time.”
Encouraged by success, the Ministry of Railways approved nationwide deployment under the Vande Bharat Mission for Smart Infrastructure.
4. Data: The New Lifeline
Over 3,000 locomotives and 9,500 coaches have been fitted with vibration and pressure sensors feeding continuous streams of data into the AI system.
Every 24 hours, the platform processes:
- 1.6 terabytes of data from rolling assets,
- 20 million sensor readings, and
- Hundreds of fault signatures per section.
The goal: to predict failure at least 48–72 hours before occurrence.
“AI is giving voice to metal,” said Dr. Pawan Goenka, Chairperson of IIT Madras Research Park.
“It listens to the vibration of a bolt like a doctor hears a heartbeat.”
5. Preventing Derailments Before They Happen
A 2023 audit by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) found that over 26% of train accidents were linked to track and mechanical failures.
The new predictive system aims to reduce this figure to below 5% within two years.
AI algorithms can detect micro-fractures and fatigue lines on tracks that human inspections often miss.
The Railways has installed AI-powered ultrasonic rail scanners at 400 critical sections nationwide.
“Safety is now data-driven,” said Railway Board Chairman Jaya Varma Sinha.
“Prevention will be our biggest investment.”
6. The Human–AI Partnership
Far from replacing engineers, the new system empowers them.
Every maintenance team now carries a “RailPad” tablet, displaying AI-generated diagnostics and recommended interventions.
The National Rail AI Training Academy in Lucknow has trained over 4,200 technicians and inspectors in data interpretation and digital maintenance protocols.
“AI doesn’t take decisions — it advises. Humans still hold the wrench,” said Chief Workshop Manager Rajesh Verma, Izzatnagar Depot.
7. International Parallels
Globally, predictive rail systems have transformed safety records in:
- Japan (Shinkansen) — zero derailments since 1964 due to predictive analytics.
- Germany (Deutsche Bahn) — 25% cost reduction in rolling stock maintenance.
- UK (Network Rail) — real-time monitoring of 30,000 km of track.
India’s model combines these global benchmarks with indigenous innovation, making it the largest AI-integrated transport maintenance network in the world.
8. Environmental Benefits
Predictive maintenance not only prevents accidents — it also reduces carbon footprint.
Fewer breakdowns mean:
- Lower fuel consumption,
- Reduced idle time at yards, and
- Longer component life.
Officials estimate annual carbon savings of over 4 lakh tonnes of CO₂, equivalent to planting 10 million trees.
9. The Economics of Prevention
The system is projected to save ₹6,200 crore annually by reducing emergency repairs, rerouting delays, and replacement costs.
A report by the National Institute of Public Finance and Policy (NIPFP) noted that every ₹1 invested in predictive maintenance yields ₹4.3 in savings over five years.
“We are monetising reliability,” said Railway Secretary Anil Kumar Lahoti.
10. The Role of RailTel and Cloud Infrastructure
RailTel Corporation of India, the Railways’ telecom arm, has built the data backbone for the predictive maintenance network.
All telemetry data flows into three regional data hubs — Delhi, Nagpur, and Bengaluru — before being processed at the Central Command Centre in Secunderabad.
This high-speed infrastructure enables instant cross-referencing of anomalies across zones, preventing cascading failures.
“If one wheel overheats in Odisha, we can flag its twin in Rajasthan within seconds,” said RailTel CTO Sunita Varma.
11. Safety Culture and AI Ethics
The Railways has emphasised that the system complies with India’s AI Ethics and Safety Framework, ensuring no decision-making without human validation.
All maintenance predictions are stored with audit trails, and black-box logs are available for investigation in case of failure.
“Accountability remains human,” said Minister Vaishnaw.
“AI helps us anticipate — not abdicate — responsibility.”
12. Predictive Stations and Smart Yards
Select yards — including Kharagpur, Itarsi, and Tughlakabad — now operate as “Smart Maintenance Hubs” where AI autonomously schedules repairs and inventory.
Drones equipped with thermal cameras conduct overhead inspections, while robotic arms handle undercarriage checks.
“Machines now maintain machines,” said S.K. Pathak, Zonal Chief Engineer.
“Our engineers oversee — not overwork.”
13. Challenges Ahead
Despite success, officials acknowledge hurdles:
- Integration with older locomotives,
- Sensor calibration in extreme climates,
- Resistance from traditional inspection staff.
To address this, the Railways has introduced an incentive-based training program and plans to retrofit 5,000 legacy engines by mid-2026.
“Transformation always meets inertia,” said Jaya Varma Sinha.
“But results will silence resistance.”
14. AI in Passenger Experience
Beyond safety, predictive analytics will soon enhance passenger comfort by monitoring AC units, lighting systems, and seat mechanisms.
Trial runs on Vande Bharat Express routes show 98% punctuality and improved reliability due to predictive interventions.
“A train that never stops unexpectedly is the best advertisement for Railways,” said Minister Vaishnaw.
15. Global Recognition
The initiative has drawn international attention.
The World Bank, Asian Development Bank, and European Investment Bank have expressed interest in co-funding India’s Rail AI Lab expansion.
“This project is a template for developing nations,” said ADB Director Kenji Hasegawa.
“It merges scale, safety, and sustainability.”
16. Public Reaction
Social media erupted with praise after the Railways shared visuals of AI dashboards predicting faults in real time.
Many called it a “turning point for Indian engineering.”
However, some unions have voiced concerns over job displacement, prompting the Ministry to assure that AI will augment, not replace manpower.
“Technology is the tool, not the target,” Vaishnaw reiterated.
17. The Human Element
At the Lucknow Workshop, 56-year-old technician Omprakash Singh inspected a bogie with a handheld AI sensor.
“Earlier, I relied on my ear. Now, the sensor listens for me,” he said.
“It tells me where the sound of danger begins.”
His story reflects India’s journey — where heritage meets hardware.
18. Safety by Design
The Railways has set an ambitious target: zero major derailments by 2027.
AI-based inspection reports are now mandatory before every long-distance train departure.
Independent safety audits will be published quarterly, reviewed by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) and the NITI Aayog AI Ethics Board.
19. Expanding Beyond India
Indian Railways is in talks with Bangladesh, Kenya, and Indonesia to export the AI maintenance model as part of the Make in India Global Railway Partnership (MiGRaP) initiative.
“India is now exporting not just engines, but intelligence,” said Piyush Goyal, former Railway Minister.
20. Conclusion: The Track to Tomorrow
For nearly two centuries, Indian Railways has been the lifeline of the nation — connecting millions through steel and time.
Now, through AI, it aims to connect those journeys with safety, precision, and foresight.
“Every wheel that turns safely is a silent victory for technology,” said Minister Vaishnaw.
“And this victory belongs to every citizen who trusts the rails.”
The rhythm of India’s progress has always echoed on its tracks — and with AI watching every bolt and beam, that rhythm just became more reliable than ever.
#IndianRailways #AIPredictiveMaintenance #RailSafety #DigitalIndia #Innovation #SmartInfrastructure #SarhindTimes



















+ There are no comments
Add yours